Responding to a request for input from the chairs of the House Ways and Means Committee and Ways and Means Tax Policy Subcommittee, The Real Estate Roundtable submitted comments on the pending expiration of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 and ways in which tax policy can support long-term investment, economic stability, and the creation of affordable housing. (Letter, Oct. 2)
Roundtable Recommendations
The letter from Roundtable President and CEO Jeffrey DeBoer urges lawmakers to ensure that any major tax legislation in 2025 retain or include:
- The reduced tax rate on long-term capital gains. The capital gains rate is critical for driving long-term real estate investment and fostering job creation. Raising capital gains rates, taxing unrealized gains, or double-taxing gains at death would deter entrepreneurship, increase costs, and reduce economic mobility.
- Tax fairness for partnerships and pass-through entities. Half of the nation’s tax partnerships are real estate-related, making these provisions vital to the industry’s success. Section 199A, which provides a 20% deduction on pass-through business income (including REIT dividend income), allows privately held businesses to compete on a level playing field with large corporations.
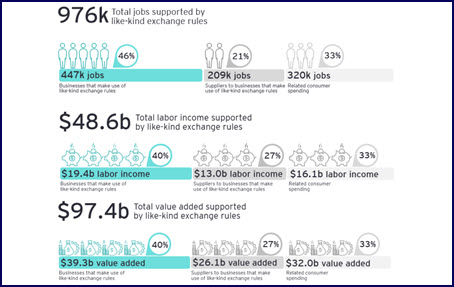
- Like-kind exchanges. Section 1031 allows for the deferral of capital gains through real estate exchanges and helps gets languishing properties into the hands of new owners who will invest in, and improve, them. Retaining section 1031 is vital to promoting reinvestment in communities, creating opportunities for minority and small business owners, and improving struggling properties.
- Tax rules that encourage, rather than deter, foreign investment in U.S. real estate. Targeted changes to the outdated and discriminatory Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act (FIRPTA) could unlock capital for large-scale real estate and infrastructure projects that create jobs and spur economic development.
- Incentives for affordable housing, energy efficiency, and community revitalization. The Roundtable supports expanding the low-income housing tax credit (LIHTC), improving the real estate-related clean energy tax provisions in the Inflation Reduction Act, and introducing new incentives for the conversion of obsolete commercial buildings into affordable housing. The letter also calls for a long-term extension of Opportunity Zone (OZ) tax incentives and preserving carried interest tax rules that recognize and reward sweat equity with capital gains treatment.
The Roundtable is committed to working with lawmakers to ensure the U.S. maintains a competitive tax code that encourages capital formation, rewards entrepreneurial risk-taking, and supports critical policy objectives, including accessible and affordable housing and safe and healthy communities.