
Congress passed compromise legislation this week to suspend the debt ceiling for two years and restrain government spending, sending it to President Biden for his signature and calming world financial markets days before a US government default. (CQ and Wall Street Journal, June 2)
After the Debt Ceiling
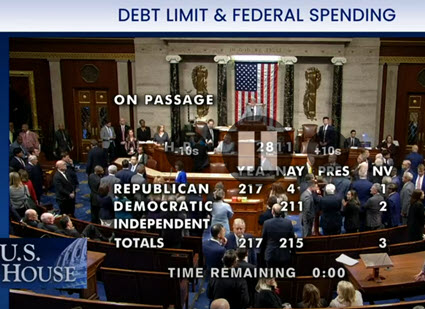
- The House on Wednesday night passed the Fiscal Responsibility Act (H.R. 3746)—forged by President Joe Biden, House Speaker Kevin McCarthy (R-CA), and their negotiation teams—to suspend the nation’s $31.4 trillion debt limit until Jan. 1, 2025 and cut spending by at least $1.5 trillion. The Senate approved the bill last night by a bipartisan vote of 63-36. (Congressional Budget Office, May 30 and Associated Press, May 26)
- “No one gets everything they want in a negotiation, but make no mistake: this bipartisan agreement is a big win for our economy and the American people,” President Biden stated last night. “I look forward to signing this bill into law as soon as possible…” (White House statement, June 1)
- House policymakers have signaled they may follow the debt ceiling crisis with a legislative tax proposal that could include significant measures affecting commercial real estate. (Roundtable Weekly, May 26)
- Congressional action on such measures would come at a time when the office sector faces difficult conditions, including asset price discovery and tighter liquidity. (Wall Street Journal, May 30 Financial Times, May 29 | GlobeSt, May 26)
Economic Conditions & CRE
- Real Estate Roundtable Chair John Fish (Chairman and CEO, SUFFOLK) explained the economic conditions facing CRE and the office market, along with other pressures such as remote work and a shortage of labor, in a May 26 Boston Globe interview. “We’re in a very precarious situation,” Fish said.
- Roundtable Board Member Ross Perot, Jr., above, (Chairman, The Perot Companies and Hillwood) discussed the financing challenges faced by some CRE sectors in an interview with Bloomberg TV on Wednesday. “If the industry can’t get a construction loan, real estate will have a recession,” Perot said. “The key to commercial real estate today will be banking.”
- The Federal Reserve’s “Beige Book” issued this week also reported on the nation’s current overall economic activity, noting, “Commercial construction and real estate activity decreased overall, with the office segment continuing to be a weak spot.” (GlobeSt, May 31)
- Additionally, Trepp’s CMBS Delinquency Report issued this week showed the nation’s overall CMBS delinquency rate hit a 14-month high, topping 4% for the first time since 2018. Although May’s delinquency rate jumped to 3.62%, up 53 basis points for the month, the all-time high registered 10.34% in July 2012 and the COVID-19 high reached 10.32% in June 2020.
- Federal Reserve monetary policies, congressional fiscal policy, potential tax measures, and other issues impacting CRE will be discussed during The Real Estate Roundtable’s Annual Meeting on June 13-14 in Washington, DC.
The Roundtable meeting includes policy advisory committee meetings—open to all members—that will feature prominent policymakers, including Senate Banking Committee Member Bill Hagerty (R-TN); House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Jason Smith (R-MO); David Crane, the US-DOE’s Director of the Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations; and Alejandra Nunez, US-EPA Assistant Administrator overseeing climate policy.
# # #










 The Real Estate Roundtable yesterday urged its membership—leaders of the nation’s top publicly held and privately owned real estate ownership, development, lending and management firms—to contact federal lawmakers to raise the nation’s debt ceiling. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said the U.S. reached the maximum amount it can legally borrow yesterday, and that “extraordinary measures” would allow the country to continue paying its bills, but only until early June. (
The Real Estate Roundtable yesterday urged its membership—leaders of the nation’s top publicly held and privately owned real estate ownership, development, lending and management firms—to contact federal lawmakers to raise the nation’s debt ceiling. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said the U.S. reached the maximum amount it can legally borrow yesterday, and that “extraordinary measures” would allow the country to continue paying its bills, but only until early June. (


