
The Real Estate Roundtable urged the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) on Wednesday to follow a newly released policy guide as the agency awards grants for states and localities to develop Building Performance Standards (BPS). The guidebook developed by the Roundtable’s Sustainability Policy Advisory Committee (SPAC) reflects RER’s ongoing commitment to addressing climate change while ensuring the economic sustainability of real estate investments and the communities they support. (Letter, Oct. 8)
Building Performance Standards (BPS)
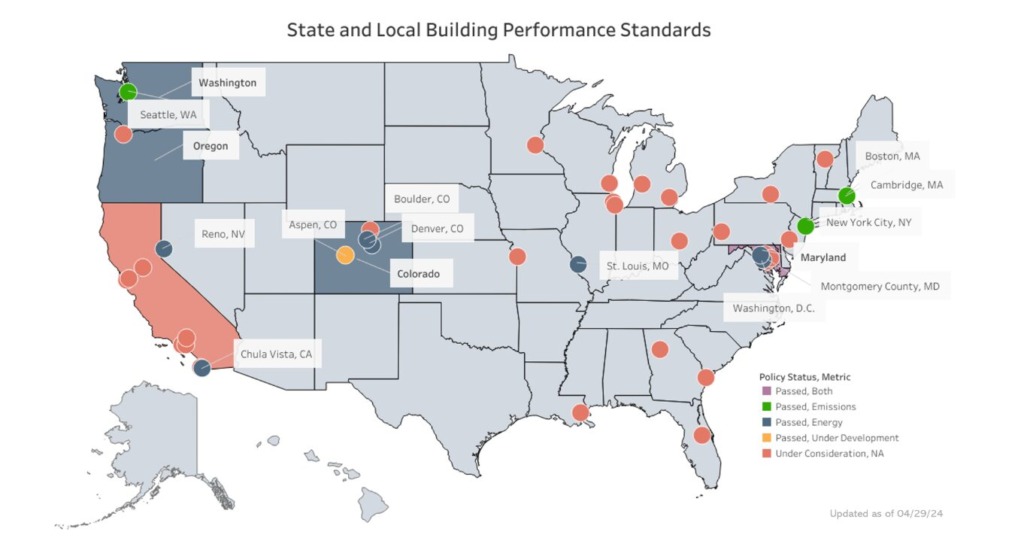
- State and local governments are increasingly adopting BPS laws that impose energy and climate performance mandates on real estate.
- These laws typically set annual limits on how much energy buildings can use and how much greenhouse gases (GHGs) they can emit, with an ultimate goal of reaching net zero emissions around 2050.
- International groups also apply pressure for energy and emissions performance limits on buildings to drive global investments in real estate. (Roundtable Weekly, July 19)
- The Department of Energy (DOE) in August announced $240 million in federal grants to help states and localities implement BPS laws. (Roundtable Weekly, Sept 6).
- The inconsistent nationwide BPS “patchwork” poses significant challenges for property owners and policymakers alike. These laws must be backed by studies and adequate resources to ensure they achieve significant emission reductions—while continuing to further parallel efforts to support the recovery of business districts and increase the supply of affordable housing.
- “Our members face a variety of local and state legislative initiatives around building performance standards which lack consistent, implementable, fact-based frameworks. The federal government has the research and analysis heft to create and maintain a voluntary system of fair, reasonable, and effective BPS guidelines to help inform these efforts ” said Anthony E. Malkin, Chair of the Roundtable’s SPAC (Chairman and CEO, Empire State Realty Trust).
- “Our peer-reviewed, 20-point policy guide intends to help start and guide a discussion of the subject,” he continued.
BPS Policy Guide: 20 Key Points
- RER’s policy guide should shape how DOE disburses tens of millions of taxpayer-funded federal grants to states and cities across the country. It outlines 20 key points that should be prioritized when developing and implementing BPS laws. These include:
- Develop science-based and data-driven standards. Policymakers should base building performance targets on robust cost-benefit analyses, housing affordability studies, grid resilience assessments, and actual data on energy usage.
- Align standards across jurisdictions. Property owners face confusing and inconsistent mandates. Policymakers should harmonize rules to ease multi-jurisdictional compliance and use landmark federal programs as a uniform means for compliance.
- Provide clear compliance resources and fair remedies. Policymakers should ensure that BPS laws come with transparent, accessible compliance pathways that building owners can follow. This includes offering practical resources, technical assistance, and incentive programs to help owners plan for “life-cycle” capital investments and retrofits. Enforcement mechanisms should offer building owners reasonable opportunities to correct non-compliance before imposing fines.
RER welcomes engagement on the 20-point policy guide to help craft BPS laws that are fair and effective.




















