The Roundtable’s policy news digest will resume publication on Friday, December 5, 2025
Recent issues of Roundtable Weekly can be searched by keyword here.
The Roundtable’s policy news digest will resume publication on Friday, December 5, 2025
Recent issues of Roundtable Weekly can be searched by keyword here.

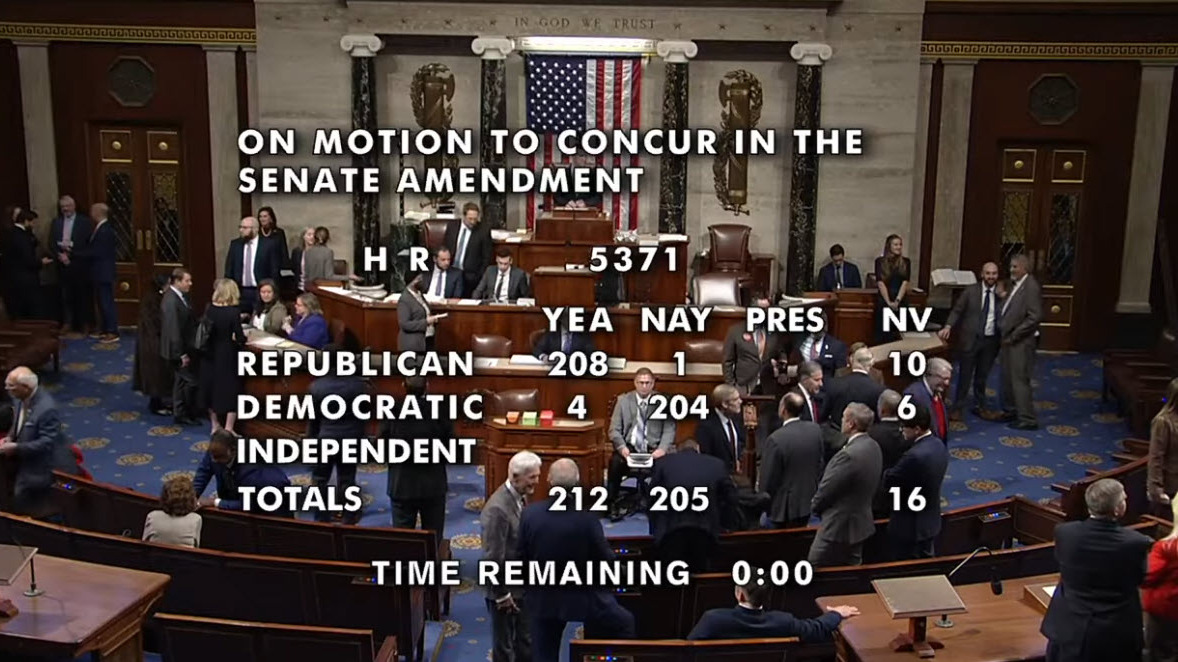
The new stopgap extends government funding only through Jan. 30, leaving appropriators less than two months to complete the remaining FY2026 bills. With the government reopened, housing, permitting, tax, and energy policy issues are again at the forefront of congressional debates. (PoliticoPro, Nov. 13)
Housing

Permitting & Energy

Tax and Tariff Policy

Roundtable on the Road

RER will continue working with lawmakers to provide insights and advance practical solutions as Congress moves into a compressed legislative window.

The federal government reopened late Wednesday after a 43-day shutdown, the longest in U.S. history, as Congress approved a short-term funding bill keeping agencies running through Jan. 30, 2026. (The Hill, Nov. 13)
State of Play
What’s Restored: NFIP, HUD Programs, Federal Services

What’s Next
Another shutdown is possible if Congress fails to meet the Jan. 30 deadline.

Blackstone announced this week that Kathleen McCarthy, global co-head of Blackstone Real Estate, will step down from the firm at the end of the year after an impactful 15-year tenure. As Chair of The Real Estate Roundtable (RER), she will continue to lead the organization’s policy agenda, member engagement and industry outreach. (Bloomberg | CoStar, Nov. 11)
Next on RER’s meeting calendar is the all-member State of the Industry (SOI) Meeting, which will include policy advisory committee sessions, on January 21–22, 2026, in Washington, DC.

The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released its long-awaited reorganization of various program offices on Monday. It lists ENERGY STAR–the voluntary federal public-private partnership promoting efficiency in buildings and appliances–as falling under the newly structured Office of Radiation and Indoor Air (“ORIA”). (EPA website | E&E News, Nov. 3)
Agency Restructuring
Industry Advocacy

ENERGY STAR Continues During Shutdown
RER and our industry partners will continue to track these events closely. The coalition will advocate for EPA to operate the bipartisan, highly successful ENERGY STAR program robustly and efficiently once the government reopens.

The government shutdown, now in its sixth week, continues to strain markets. Despite some bipartisan progress, the path to reopening remains uncertain as the economic fallout spreads across housing, infrastructure, and other sectors.
State of Play
Implications for the Economy & CRE
Supreme Court Weighs Limits on Presidential Tariff Powers

RER continues to urge Congress to move swiftly toward a bipartisan funding agreement that reopens the government, restarts critical permitting and data functions, and ensures continuity for housing, infrastructure, and financial programs essential to real estate investment and economic growth.
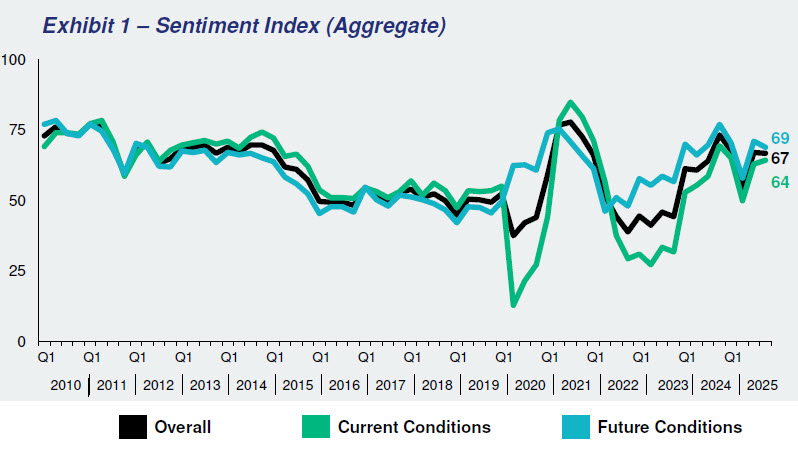
The Real Estate Roundtable’s (RER) Q4 2025 Sentiment Index registered an overall score of 67, equivalent to the prior quarter, reflecting that commercial real estate executives’ sentiment has shifted from caution toward guarded optimism as markets stabilize, transaction activity resumes, and expectations build for easing interest rates in 2026.
Topline Findings
The Q4 Sentiment Index topline findings include:
Roundtable View
Data for the Q4 survey was gathered by Chicago-based Ferguson Partners on RER’s behalf in October. See the full Q4 report.

Industry leaders convened with policymakers at this week’s Fall Roundtable Meeting to address national policies impacting commercial real estate and the broader economy.
Fall Roundtable Meeting

Speakers & Policy Issues
Roundtable members engaged in policy issue discussions with the following guests:





Next on RER’s meeting calendar is the all-member State of the Industry (SOI) Meeting, which will include policy advisory committee sessions, on January 21–22, 2026, in Washington, DC.

The Federal Reserve on Wednesday approved a second consecutive quarter-point rate cut, lowering the federal funds rate to 3.75-4 percent. Chair Jerome Powell cautioned that another reduction in December is uncertain, suggesting the pace of easing could soon slow.
Fed’s Decision
Housing and CRE Outlook
RER Advocacy

Basel III Endgame
RER will continue to track developments on monetary policies and support measures that preserve liquidity and lending capacity as rate relief remains gradual.

The federal government shutdown, now nearing its fifth week and on pace to become the longest in U.S. history, is showing early signs of bipartisan negotiation after weeks of stalemate. Lawmakers are facing mounting pressure to reach an agreement before critical deadlines affect food assistance and healthcare programs.
State of Play
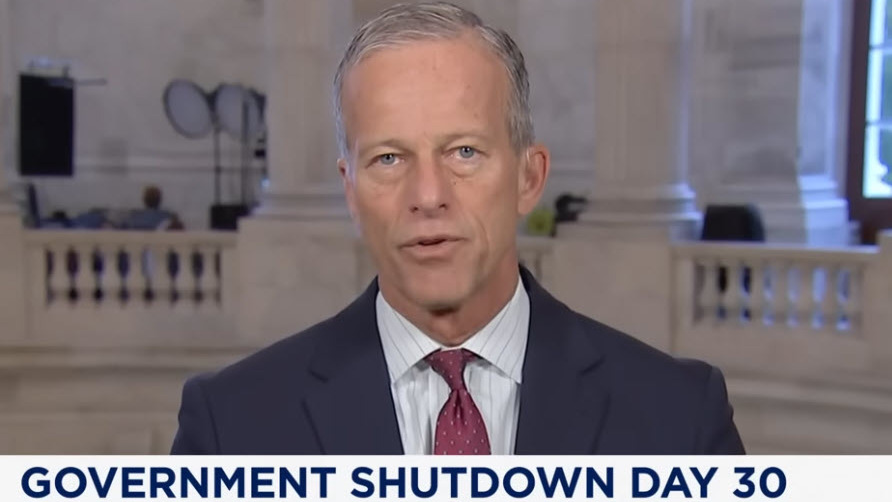
Economic Fallout

Path Forward
RER continues to urge Congress to act responsibly to reopen the government and restore critical housing, insurance, and economic programs essential to real estate investment and growth.