A new report released this month warns that proposed tax increases on carried interest could significantly harm the U.S. economy, increase the federal deficit, and jeopardize millions of jobs.
Report Findings
- The comprehensive new report by Dr. Charles Swenson, Professor of Accounting at the University of Southern California Marshall School of Business, Economic Impact on the Private Funds and Real Estate Industries Due to Potential Increases in Tax on Carried Interest, estimates what will happen if lawmakers recharacterize all carried interest income as ordinary income.
- “This report is a testament to the importance of backing up policy recommendations with sound calculations and analysis before making decisions that would affect so many American workers, small businesses, and industries,” said Dr. Swenson. (One-Pager)
- The report warns that increasing taxes on carried interest would result in:
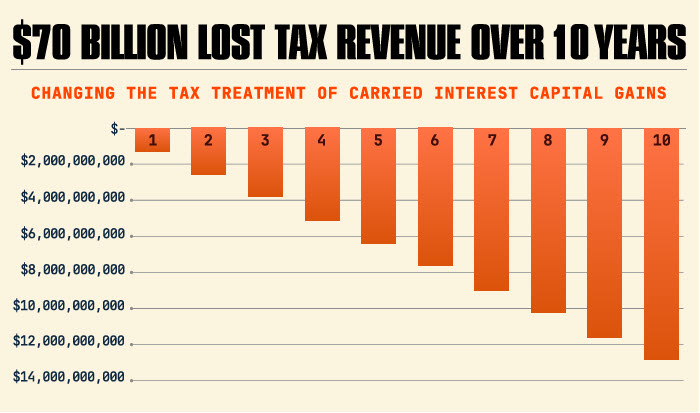
- Higher Federal Deficit: Raising taxes on carried interest could cost the U.S. government up to $70 billion in lost revenue over the next decade.
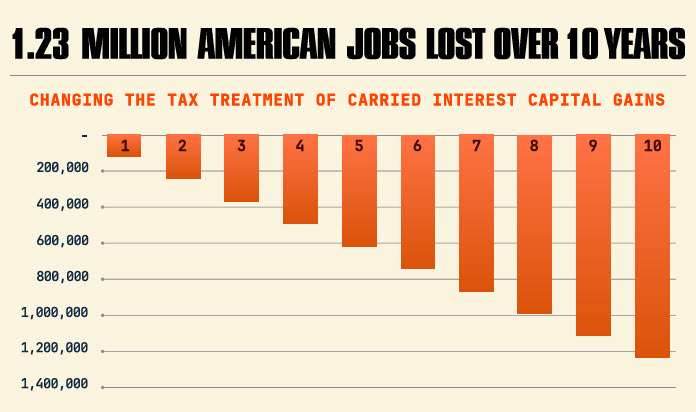
- Job Losses: Real estate, venture capital and private equity partnerships support an estimated 32 million American jobs. The private sector could lose an estimated 1.23 million jobs as businesses lose access to a critical tool for attracting capital and securing investment.
- Global Competitive Disadvantage: The proposed tax increase would raise the U.S. tax rate on many businesses and investments to 40.8% – higher than China, Canada, and numerous European countries, discouraging foreign and domestic investment.
- Worsening Housing Crisis: Higher taxes could exacerbate the current housing shortage, stalling construction at a critical time when the U.S. needs 5.5 million new units to meet demand.
- Declining Innovation: Removing the tax incentive alignment between entrepreneurs and investors would shift investments away from high-risk opportunities, particularly in high-tech and biotechnology industries.
- Lost Retirement Earnings: Public pension funds supporting over 34 million workers could lose up to $520 million annually as they’re forced into lower-yielding investments.
Industry Response
- Industry leaders reiterated the report’s findings and warned of the harmful economic consequences of increasing taxes on productive, job-supporting investment. (Press Release, April 8)
- Since carried interest and its tax treatment first emerged as a controversial political issue in 2007, RER has consistently opposed legislative proposals to tax all carried interest at ordinary income rates. (Axios, March 24 | NYT, March 8)
- President Trump revived calls to close the “carried interest tax deduction loophole” earlier this year during meetings with Republican lawmakers, framing it as a potential revenue offset. While he hasn’t mentioned it publicly in recent weeks, the issue remains part of broader GOP tax discussions. (Politico, April 25)
- In March, a coalition of 17 national real estate organizations wrote to congressional leadership urging preservation of current law on carried interest, highlighting that taxing all carried interest as ordinary income would raise taxes on 2.2 million real estate partnerships and nearly 9.7 million partners, potentially stalling new housing, infrastructure, and redevelopment projects. (RW, March 28)
- Jeffrey DeBoer, President and CEO of RER: “The new study by Professor Swenson is further evidence that recharacterizing this long term ‘carried interest’ capital gain as ordinary income would penalize entrepreneurs, slow housing production, and reduce investment in long-neglected neighborhoods. Construction costs and the risks of real estate development continue to rise and financing remains challenging. Now is not the time to raise taxes on U.S. real estate,” DeBoer said. (Press Release, April 8)
With the House having approved a $5.3 trillion budget resolution, tax legislation is now on the horizon. This timely study provides critical data on the potential consequences of changing carried interest tax treatment.



















