 Legislation aimed at increasing the nation’s supply of affordable housing was introduced by Senate and House tax writers this week while the National Multifamily Housing Council (NMHC) and National Apartment Association (NAA) offered joint testimony before a March 7 Senate Finance Committee hearing on “Tax Policy’s Role in Increasing Affordable Housing Supply for Working Families.” (NMHC President Sharon Wilson Géno, above and MarketWatch, March 9)
Legislation aimed at increasing the nation’s supply of affordable housing was introduced by Senate and House tax writers this week while the National Multifamily Housing Council (NMHC) and National Apartment Association (NAA) offered joint testimony before a March 7 Senate Finance Committee hearing on “Tax Policy’s Role in Increasing Affordable Housing Supply for Working Families.” (NMHC President Sharon Wilson Géno, above and MarketWatch, March 9)
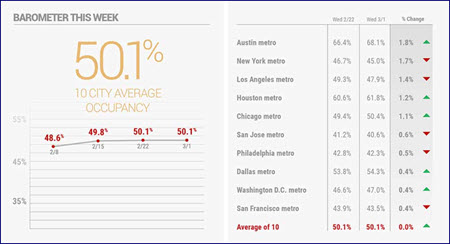
Solutions to Meet the Need
- A new report from real estate brokerage Redfin shows that the number of affordable home listings fell 53% from last year—the largest annual drop in Redfin’s records, which date back to 2013. (The Hill and Redfin news release, March 3)
- The National Low Income Housing Coalition estimates there is a shortage of 7 million affordable and available rental homes in the United States, while a Rosen Consulting Group study reports the underbuilding gap is 5.5 million units.
- This week’s Senate hearing displayed bipartisan policymaker consensus on the need to increase the supply of affordable housing by expanding the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) and other tax incentives. (TaxNotes, March 8 and Congressional Research Service, “An Introduction to the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit”)
- During the hearing, NMHC President Sharon Wilson Géno offered joint testimony that included recommendations to address the affordable housing crisis, including tax policy, regulatory reform, rental assistance, and development incentives. (NHMC News | Video of Géno’s remarks and Written testimony, March 7)
Senate Bills 
- Senate Finance Committee Chairman Ron Wyden (D-OR), above, noted his support for the Affordable Housing Credit Improvement Act (AHCI), the Neighborhood Homes Investment Act, and the reintroduction of the Decent, Affordable, Safe Housing for All (DASH) Act in his opening comments.
- Wyden’s DASH Act would strengthen the LIHTC and offer a new Middle-Income Housing Tax Credit (MIHTC) that would provide a tax credit to developers who house tenants between 60 and 100% of the area’s median income. (DASH Act Text | Bill Summary | Section-by-section)
- The AHCI would expand the pool of tax credits allocated to states for new affordable housing, make it easier to combine LIHTC with other sources of capital like private activity bonds, and facilitate LIHTC rehab projects.
- Wyden added in his opening comments, “Members of Congress also need to keep pushing state and local authorities to cut back on the thicket of zoning rules that get in the way of building the housing Americans need.”
- The Roundtable has supported these Senate bills since they were introduced last year. Real Estate Roundtable President and CEO Jeffrey DeBoer previously stated, “Overly restrictive land-use and zoning policies, construction cost increases, and labor shortages are deepening our housing challenges, which now extend across the entire country. Government at all levels needs to be part of the solution, not part of the problem.” (Roundtable Weekly, July 22, 2022)
House Action 
- Reintroduction of similar LIHTC legislation in the House is expected by Reps. Suzan DelBene (D-WA) and Brian Higgins (D-NY). (BGov, March 2)
- Additionally, House Ways and Means Tax Subcommittee Chair Mike Kelly (R-PA) and committee member Jimmy Panetta (D-CA) on March 1 reintroduced the More Homes on the Market Act, which would double the capital gains exclusion for home sellers to $500,000 for single individuals and $1 million for married couples. (TaxNotes, March 8)
Despite widespread congressional support for certain affordable housing legislation, prospects for the bills are uncertain until the national debt ceiling issue is addressed—and a tax legislative package is identified that could include such measures.
# # #










 Tax provisions affecting individuals and small businesses originally enacted as part of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017—along with the state and local tax (SALT) deduction cap—would be made permanent under legislation reintroduced this month by House Ways and Means Committee Vice Chairman Vern Buchanan (R-FL), above. (
Tax provisions affecting individuals and small businesses originally enacted as part of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017—along with the state and local tax (SALT) deduction cap—would be made permanent under legislation reintroduced this month by House Ways and Means Committee Vice Chairman Vern Buchanan (R-FL), above. (

